
Change the numbers in any box and the graph will update automatically. N(T) is the total number of possible outcomes. The figure below shows the graph of an F distribution. N(B) is the number of outcomes in the event B, N(A) is the number of outcomes in the event A, P(A | B) is the probability that event A occurs, given that event B has occurred, P(A ∪ B) is the probability that events A or B occur, For example, if we wish to find out the variability in the IQ scores of females vis-vis males. It measures the degree of diversity between two data sets. It will calculate the probability density function or the Cumulative Distribution Function for the F Distribution. P(A ∩ B) is the probability that events A and B both occur, The F.DIST Function 1 is categorized under Excel Statistical functions. F distribution F (x,1,2) (1)probability density f(x,1,2) 1 2 1 2 2 2 B(1 2,2 2) x1 2 1 (2+1x)1+2 2 (2)lower cumulative distribution P (x,1,2) x 0 f(t,1,2)dt (3)upper cumulative distribution Q(x,1,2) x f(t,1,2)dt F d i s t r i b u t i o n F ( x, 1, 2) ( 1) p r o b a b i l i t y d e n s i t y f ( x, 1, 2) 1 1 2 2 2 2 B ( 1 2. This feature of the F-distribution is similar to both the t -distribution and the chi-square. The particular F-distribution that we use for an application depends upon the number of degrees of freedom that our sample has. This means that there is an infinite number of different F-distributions. The distribution is also known as positive values, similar to the distribution of X2. The F-distribution is a family of distributions. Here is we describe that F-distributed errors are common in the analysis of variance, which is widely used in the social sciences. It can be shown to follow that the probability density function (pdf) for X is given by. where and are independent random variables with chi-square distributions with respective degrees of freedom and. The calculator will generate a step by step explanation along with the graphic representation of the data sets and regression line. The F-distribution with d1 and d2 degrees of freedom is the distribution of. the qf() to calculate the quantile for a given area ( probability) under. P(B') is the probability that event B does not occur, Choose the F-distribution and enter the degrees to calculate the critical value for the F-statistic which is (n 1). Enter a probability distribution table and this calculator will find the mean, standard deviation and variance. We use the df() to calculate the density at the value of 1.2 of a F-curve with. P(B) is the probability that event B occurs,
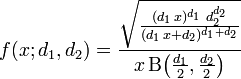
P(A') is the probability that event A does not occur,

P(A) is the probability that event A occurs, The Multiple Event Probability Calculator uses the following formulas: Results Multiple Event Probability Value (decimal) Value (percent) P(A) - P(A') - P(B) - P(B') - P(A ∩ B) - P(A ∪ B) - P(A | B) - P(B | A) - Probability Formulas Multiple Event Probability Calculator (A & B are independent events)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
